“贫居闹市无人问,富在深山有远亲。”
正文
源码:\sources\Android-25
PriorityQueue通过名字也可以看的出来,是优先队列,PriorityBlockingQueue是优先阻塞队列,这两个类其实方法都差不多,只不过PriorityBlockingQueue操作的时候会加锁ReentrantLock,PriorityQueue操作的时候是没有加锁的,代码也不多,简单看一下,主要以PriorityQueue中的方法为主,会有部分PriorityBlockingQueue类的方法先看一个构造方法
PriorityQueue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
/**
* Creates a {@code PriorityQueue} with the specified initial capacity
* that orders its elements according to the specified comparator.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity for this priority queue
* @param comparator the comparator that will be used to order this
* priority queue. If {@code null}, the {@linkplain Comparable
* natural ordering} of the elements will be used.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code initialCapacity} is
* less than 1
*/
public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity,
Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
// Note: This restriction of at least one is not actually needed,
// but continues for 1.5 compatibility
if (initialCapacity < 1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.queue = new Object[initialCapacity];//初始化空间
//比较器,可以为空,如果为空,queue中的元素要实现Comparable接口
this.comparator = comparator;
}
构造方法比较多,这里只;列出了其中的一个,这个没啥可说的,下面再看初始化集合的方法initElementsFromCollection
initElementsFromCollection
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
// 从集合c中初始化元素
private void initElementsFromCollection(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
// If c.toArray incorrectly doesn't return Object[], copy it.
//copy集合c到数组a中
if (a.getClass() != Object[].class)
a = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length, Object[].class);
int len = a.length;
if (len == 1 || this.comparator != null)
for (Object e : a)
if (e == null)//不允许为null
throw new NullPointerException();
this.queue = a;//copy的元素
this.size = a.length;//数组的大小
}
这个方法是私有的,下面来看一个调用它的方法initFromCollection
initFromCollection
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
/**
* Initializes queue array with elements from the given Collection.
*
* @param c the collection
*/
private void initFromCollection(Collection<? extends E> c) {
initElementsFromCollection(c);
//初始化完成之后,要重新建堆
heapify();
}
继续看一下heapify方法,
heapify
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
/**
* Establishes the heap invariant (described above) in the entire tree,
* assuming nothing about the order of the elements prior to the call.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void heapify() {
//从插入元素的最后一个节点的父节点位置开始调整,这里可能不太好理解的是i和size之间的关系,
//正常情况下父与子的关系left(i)=2i+1,right(i)=2i+2;(这里的i是数组下标),这里的size是数组的
//长度,这里从i开始调整有个好处,就是下面的每次调整都会让父节点成为最小的,所以到后面的时候不需要
//每次都循环到叶子节点,大大减少了循环的次数,如果从0开始,就不会有这样的好处了
for (int i = (size >>> 1) - 1; i >= 0; i--)
siftDown(i, (E) queue[i]);
}
注释都在代码中,不用再过多介绍,下面看一下另一个方法,grow(int minCapacity)
grow
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
/**
* Increases the capacity of the array.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
//增加空间
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
// Double size if small; else grow by 50%
//如果原来空间小于64,则增加2,否则扩大一倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((oldCapacity < 64) ?
(oldCapacity + 2) :
(oldCapacity >> 1));
// overflow-conscious code
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)// 如果太大,则要重新调整
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);
}
grow是根据传进来的最小空间来初始化数组大小,其中hugeCapacity表示如果初始化空间太大,则需要重新调整size的大小。继续看下面的方法,add,其实他调用的是offer方法,下面看一下offer方法
offer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this priority queue.
*
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified element cannot be
* compared with elements currently in this priority queue
* according to the priority queue's ordering
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {//插入元素
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)//如果空间太小
grow(i + 1);//增加空间
size = i + 1;//size加1
if (i == 0)
queue[0] = e;//如果原来没有元素,则直接添加
else
//添加,向上调整,添加的虽然是在数组中,但是可以把它想象成为一颗二叉树,
//添加的时候是添加到数组的最后,相当于二叉树的叶子节点,因为是需要调整的,所以需要往上调整,
//这个待会可以看一下下面的siftUp方法
siftUp(i, e);
return true;
}
不多说,直接看siftUp方法
siftUp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
/**
* Inserts item x at position k, maintaining heap invariant by
* promoting x up the tree until it is greater than or equal to
* its parent, or is the root.
*
* To simplify and speed up coercions and comparisons. the
* Comparable and Comparator versions are separated into different
* methods that are otherwise identical. (Similarly for siftDown.)
*
* @param k the position to fill
* @param x the item to insert
*/
private void siftUp(int k, E x) {//根据是否有比较器,旋转哪种调整方式
if (comparator != null)
siftUpUsingComparator(k, x);
else
siftUpComparable(k, x);
}
没什么悬念,一个是有比较器的,一个是没有的,两个方法差不多,下面随便挑一个看一下siftUpUsingComparator方法,
siftUpUsingComparator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void siftUpUsingComparator(int k, E x) {
//(1)往上调整,注意这里的x不一定是下标为k的元素,如果不明白,可以看一下下面的removeAt方法接知道。
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;//k位置的父节点的下标
Object e = queue[parent];// 父元素
//如果当前的比父的大就不需要调整了,直接退出循环,因为父节点是小于子节点的
if (comparator.compare(x, (E) e) >= 0)
break;
//父子交换
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = x;// 把x放入高指定位置
}
如果上面的注释还看不明白,待会下面通过一张图来说明,然后再看一个向下调整的siftDownUsingComparator
siftDownUsingComparator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void siftDownUsingComparator(int k, E x) {
int half = size >>> 1;
//(2)这里为什么没有等于,因为size不是下标,是数组的长度,half所在的元素其实就是叶子节点,
//只有k所在元素有子节点的时候才会调整,如果没有子节点就没法往下调整,所以如果等于没有意义,
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1;//默认是左子节点
Object c = queue[child];//默认是左子节点
int right = child + 1;//右子节点
//比较左右两个节点,把小的保存到c中
if (right < size &&
comparator.compare((E) c, (E) queue[right]) > 0)
c = queue[child = right];
//如果x比连个子节点都小,就没有必要往下调整了,直接返回
if (comparator.compare(x, (E) c) <= 0)
break;
//把最小的存储到k,然后循环
queue[k] = c;
k = child;
}
queue[k] = x;//把x插入到查找的k位置。
}
这两个方法才是这个类的主要的方法,没什么难度,下面画个图,更容易理解上面的(1)和(2)分别对应下面的图(1)和(2)。
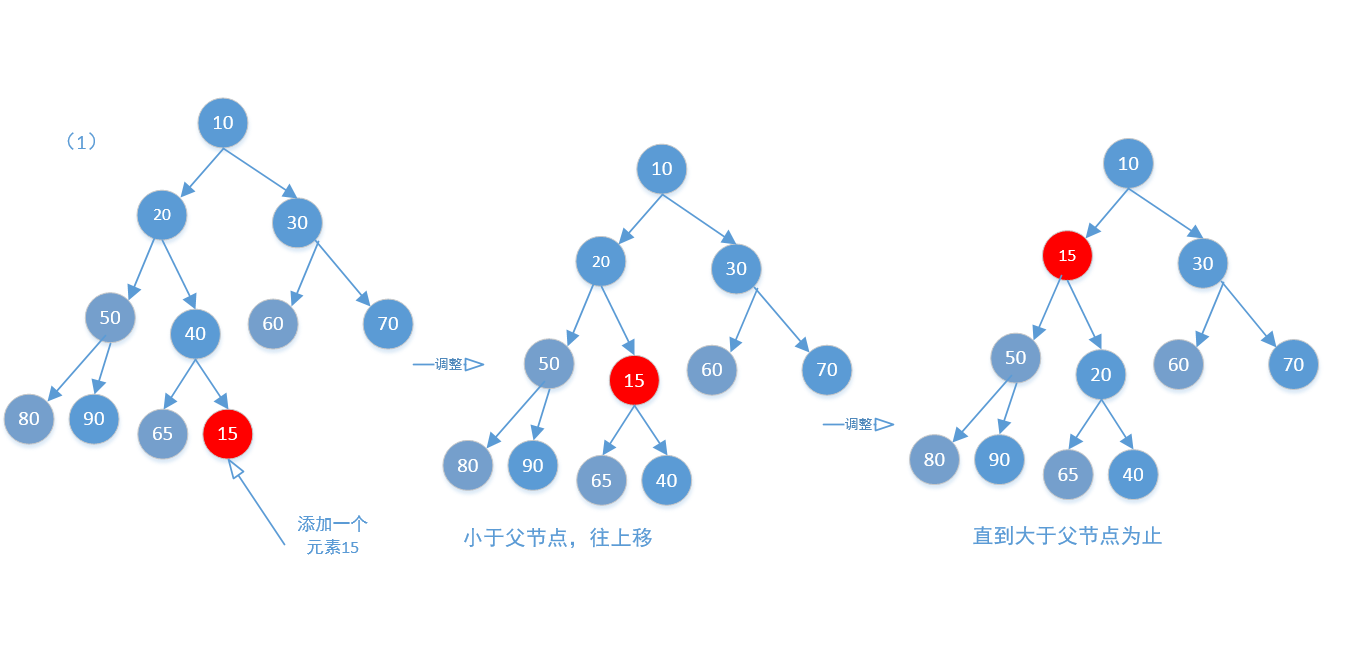
添加的时候是从最后一个添加的,也就是叶子节点,但往上调整并不是每次都是从最后的叶子节点开始的,还有移除等方法都有可能调用这个方法,其实原理都一样,把当前需要调整的节点和父节点对比,如果小于父节点就交换,如果大于停止循环,不要交换,OK,下面再来看一下往下调整的方法图
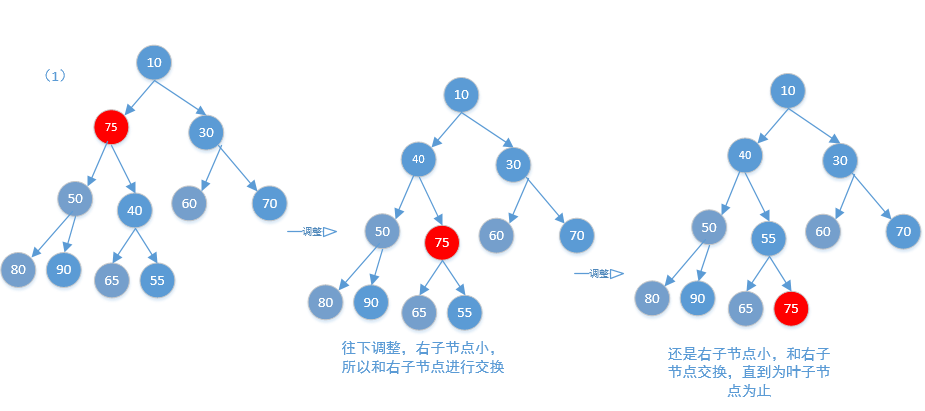
OK,下面再看另一个方法poll(),表示获取二叉树的根元素
poll
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
//获取第一个元素,也就是二叉树的根
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E poll() {
if (size == 0)
return null;
int s = --size;// size减1
modCount++;
E result = (E) queue[0];//移除的元素,
E x = (E) queue[s];//最右一个元素
queue[s] = null;//让最后一个为空
if (s != 0)
siftDown(0, x);//往下调整
return result;
}
接着看,下一个removeAt
removeAt
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
/**
* Removes the ith element from queue.
*
* Normally this method leaves the elements at up to i-1,
* inclusive, untouched. Under these circumstances, it returns
* null. Occasionally, in order to maintain the heap invariant,
* it must swap a later element of the list with one earlier than
* i. Under these circumstances, this method returns the element
* that was previously at the end of the list and is now at some
* position before i. This fact is used by iterator.remove so as to
* avoid missing traversing elements.
*/
// 移除下标为i的元素
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E removeAt(int i) {
// assert i >= 0 && i < size;
modCount++;
int s = --size;
if (s == i) // removed last element
queue[i] = null;//如果是最后一个直接删除,不需要在调整,因为最后一个在二叉树中是叶子节点
else {
E moved = (E) queue[s];//记录最后一个元素
queue[s] = null;//然后把最后一个元素的位置置null
//从i位置开始往下调整,相当于把最后的moved放到i位置上然后调整,
siftDown(i, moved);
if (queue[i] == moved) {
//如果往下调整的时候下面的两个子节点都比他大,是调整不了的,所以需要在往上调整,
siftUp(i, moved);
if (queue[i] != moved)
return moved;
}
}
return null;
}
OK,到目前为止,基本上分析完毕。